Jordan: A hot air mass gradually affects the Kingdom at the end of the first week of September
Arabia Weather - The latest weather maps through computer simulation models indicate that the Levant, including Jordan, will be affected by a hot air mass at the end of the first week of September, causing a gradual rise in temperatures in all regions, and the dominance of extremely hot weather with the weekend.
Monday and Tuesday...a rise in temperatures, with normal summer weather remaining
It is expected that temperatures will tend to rise slightly in the Kingdom during the middle of this week, and thus be slightly higher than their usual levels for this time of the year, and thus normal summer weather will prevail in most regions of the Kingdom, while it will be hot to very hot in the desert and The Jordan Valley, the Dead Sea and Aqaba areas.
During the night hours, the weather is generally pleasant over the high mountain heights, and moderate in the rest of the regions.
The Kingdom will be affected by a gradually hot air mass towards the end of this week
It is expected, God willing, that a hot air mass will approach the Kingdom on Wednesday and Thursday, so that temperatures will continue to rise and thus become several degrees Celsius higher than their usual rates for this time of year, and the weather will turn to become relatively hot in most regions of the Kingdom, and intense. Heat in the desert, the Jordan Valley, the Dead Sea, and Aqaba.
With the weekend, the effect of the hot air mass on the Kingdom deepens, and thus temperatures continue to rise and reach the end of the thirties Celsius in the neighborhoods of the capital and most Jordanian cities, with an atmosphere described as hot during the day, while it is very hot in the desert and areas. The Jordan Valley, the Dead Sea, and Aqaba, reaching the mid-40s.
Night temperatures also continue to rise compared to what is the case, with hotter than usual conditions prevailing, but they tend to be moderate, especially over high mountains in the late hours of the night.
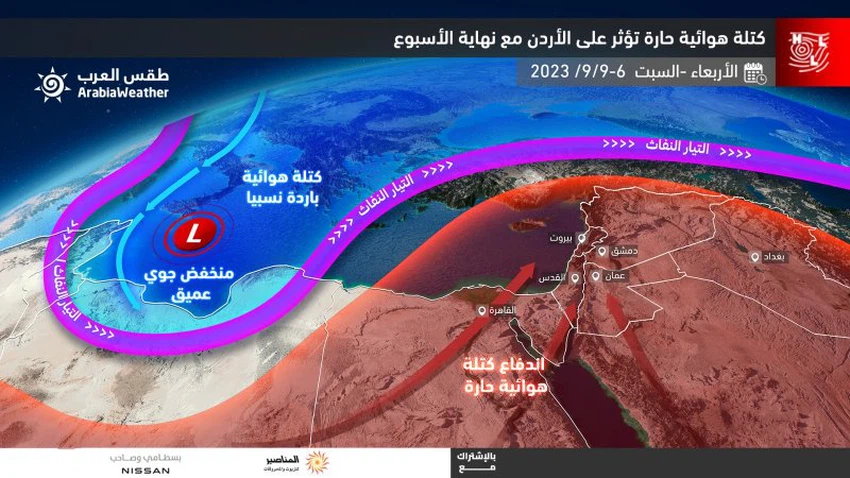
The scientific reason for expectations of a hot mass eruption into the Levant, and is it considered normal?
The expectations of a hot mass rushing into the Levant, including the Kingdom, come as a result of an early maturity in the weather systems in the central Mediterranean, meaning the early decline of relatively cold air masses from Europe towards those regions, causing the advance of southwesterly air currents this time coming from the Egyptian desert towards the Kingdom. As the cold air that rushes to the central Mediterranean Sea is met with, as a reaction to that, hot air rushes from the African Sahara towards the eastern basin of the Mediterranean Sea, including the Levant.
When reviewing the archived weather maps at “Arab Weather,” we notice that Jordan is affected in many years by hot air masses during the month of September, but they are less durable and intense when compared to those affecting the months of July and August.
God knows.
Arabia Weather App
Download the app to receive weather notifications and more..



